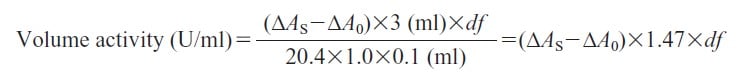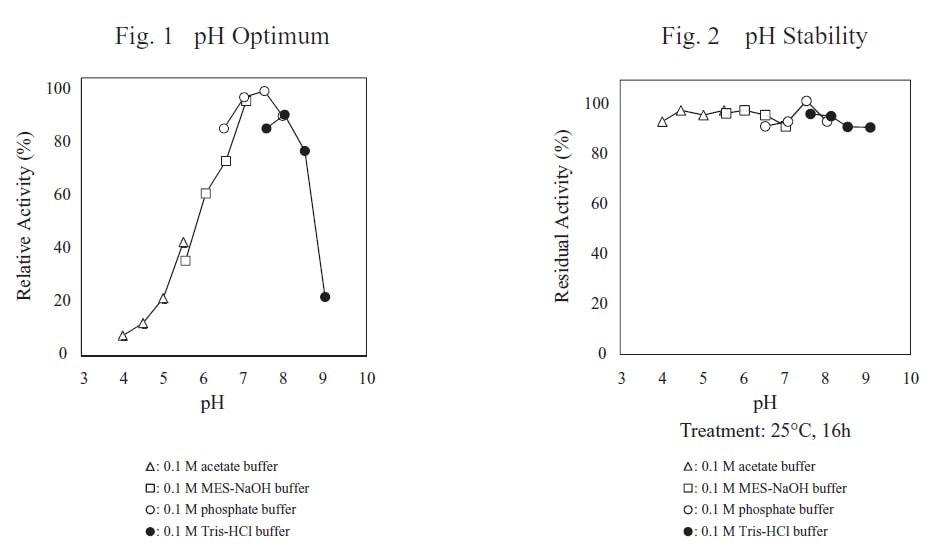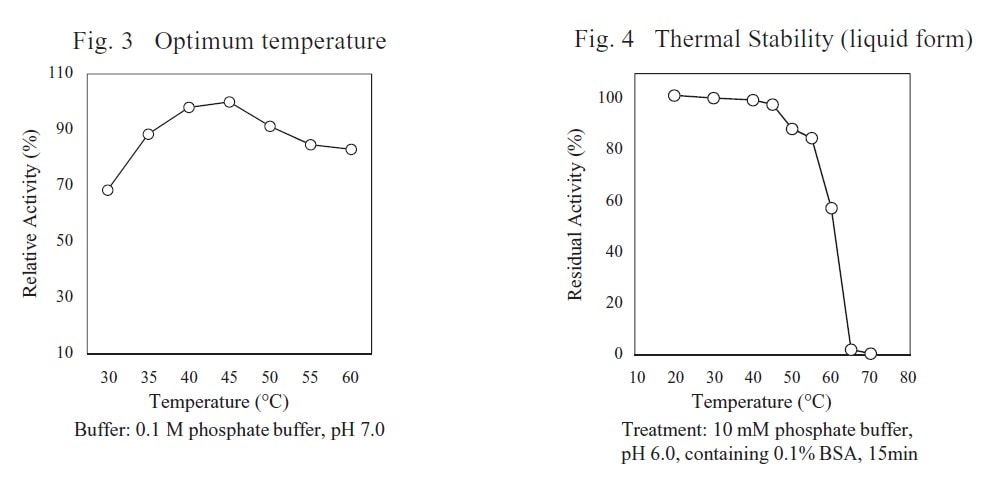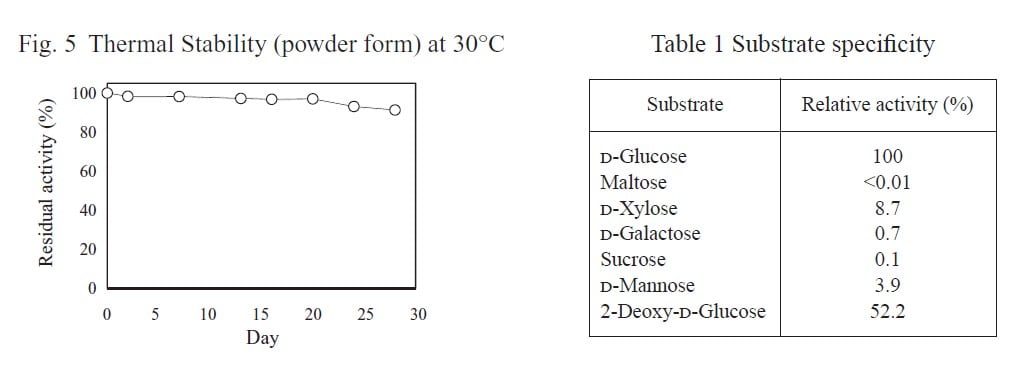
CD : 60101
The enzyme is useful for the determination of D-glucose in clinical analysis and self-monitoring blood glucose meters.
| Systematic name | D-Glucose : acceptor 1-oxidoreductase |
|---|---|
| Reaction formula | D-Glucose + acceptor →→→ D-Glucono-1,5-lactone + reduced acceptor |