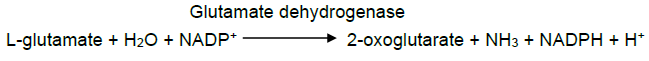
CD : 61243
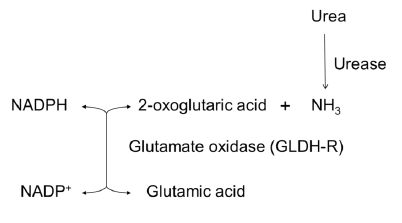
The enzyme is useful for BUN (blood urea nitrogen) test and elimination of free ammonia.
| Origin | microorganism |
|---|---|
| Systematic name | L-Glutamate: NADP+ oxidoreductase (deaminating) |
| EC Number | 1.4.1.4 |
| Reaction formula | L-glutamate + H2O + NADP+ = 2-oxoglutarate + NH3 + NADPH + H+ |