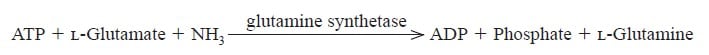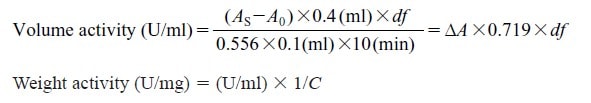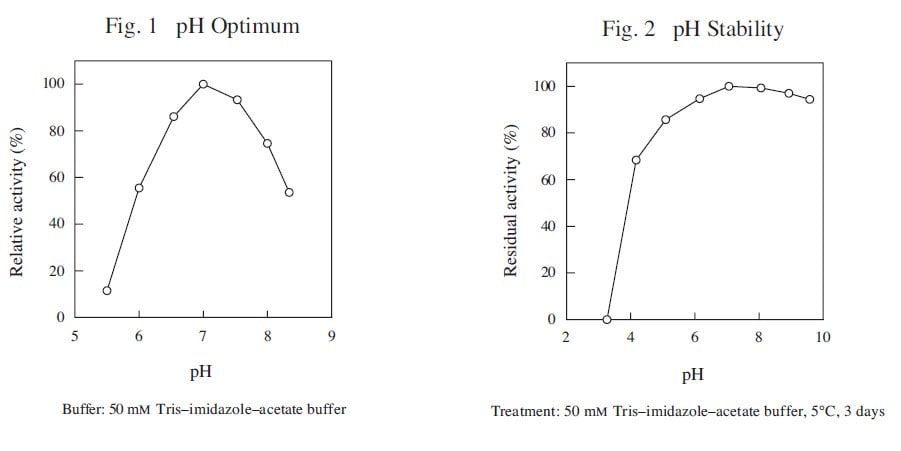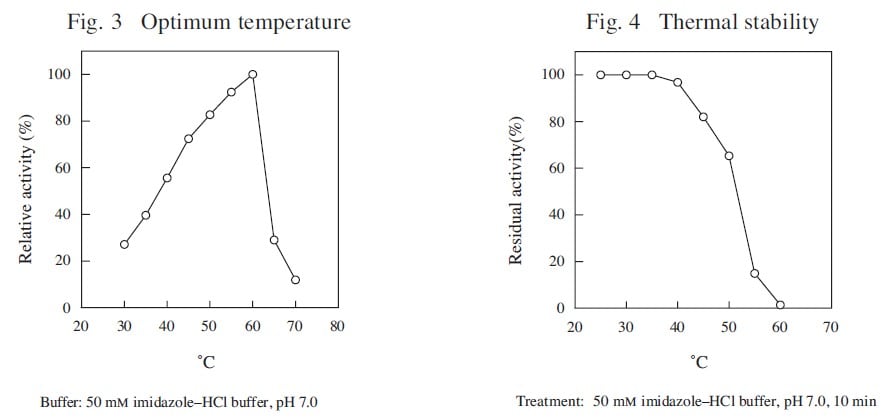
CD : 61222
The enzyme is useful for the determination of ammonia and ATP in clinical analysis.
| Origin | microorganism |
|---|---|
| Systematic name | L-Glutamate : ammonia ligase (ADP-forming) |
| EC Number | 6.3.1.2 |
| Reaction formula | ATP + L-Glutamate + NH3→→→ ADP + Orthophosphate + L-Glutamine |