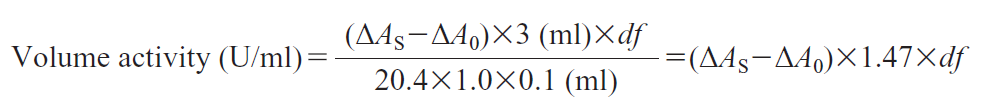CD : 60100
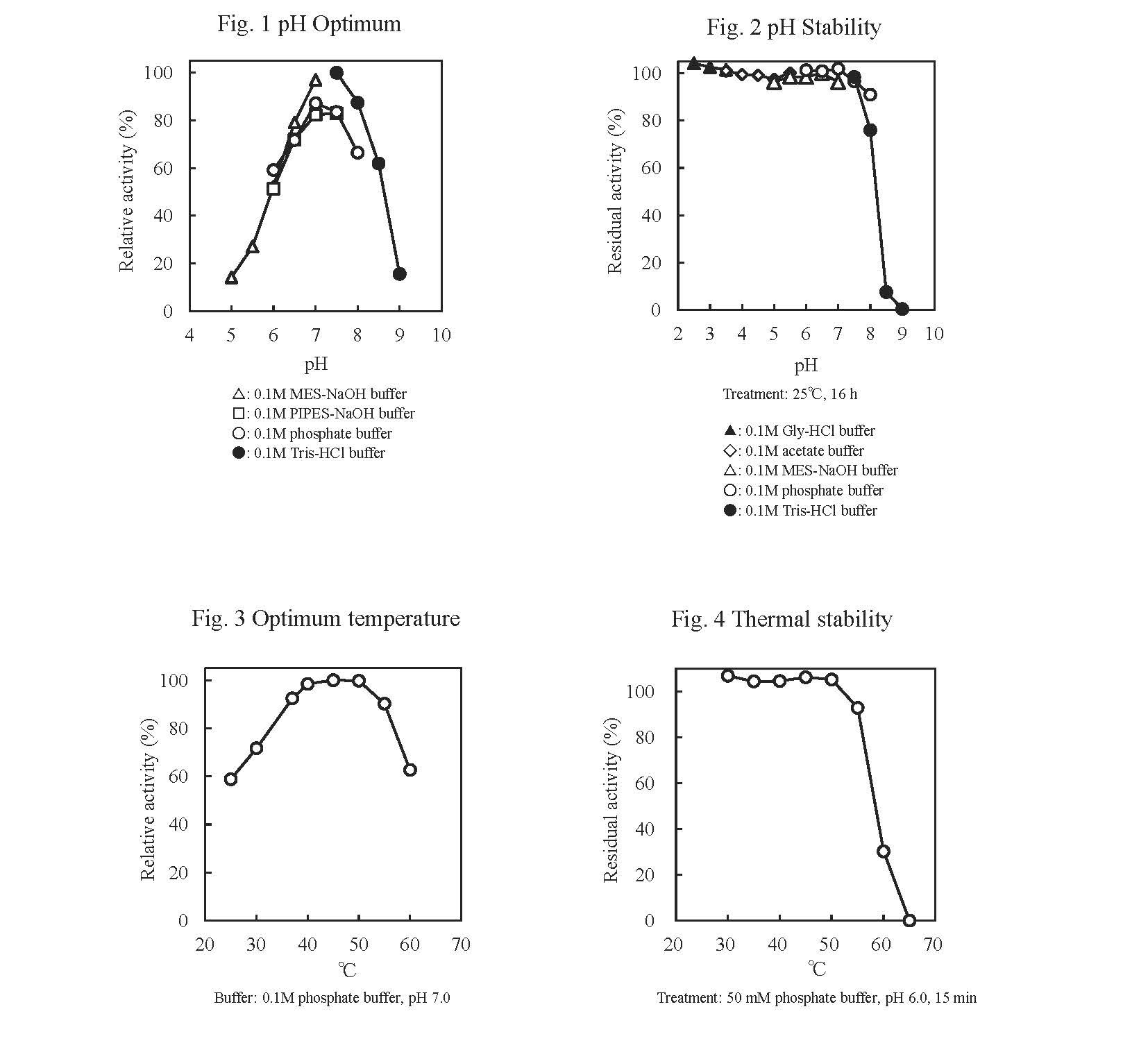
FADGDH-AA is an FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase with low reactivity toward maltose and xylose. It has high stability and maintains its reactivity even at low temperatures.
| Origin | recombinant A. sojae |
|---|---|
| Systematic name | D-Glucose : acceptor 1-oxidoreductase |
| EC Number | 1.1.5.9 |
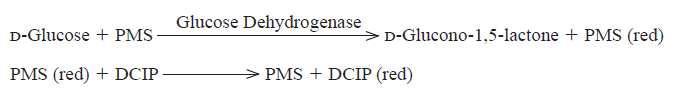
| Reaction formula | D-Glucose + acceptor →→→ D-Glucono-1,5-lactone + reduced acceptor |