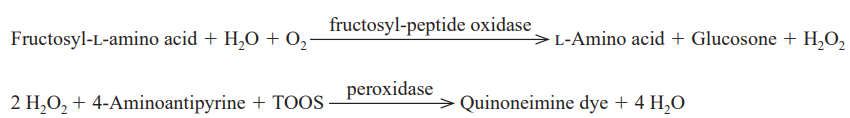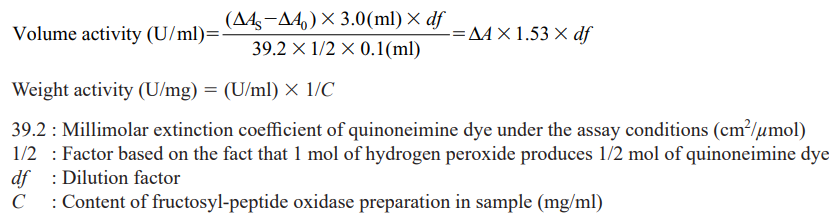
CD : 60123
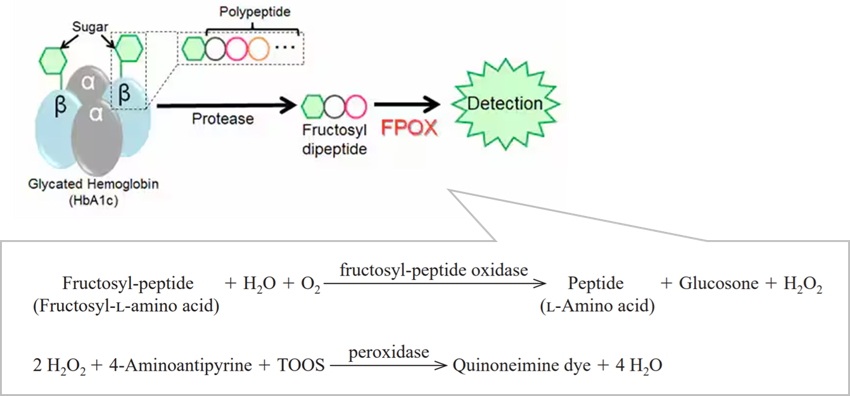
The enzyme is useful for the determination of fructosyl-peptide and fructosyl-L-amino acid. Also it is useful for the determination of HbA1c by using protease together. (HbA1c is used as a test makar to diagnose diabetes. HbA1c can also be quantified by measuring the fructosyl peptide or fructosyl-L-amino acid excised by the protease from HbA1c.)
| Origin | recombinant E. coli |
|---|---|
| Systematic name | Fructosyl-peptide : oxygen oxidoreductase |
| EC Number | 1.5.3 |
| Reaction formula | Fructosyl-L-amino acid + H2O + O2 →→→ Peptide + Glucosone + H2O2 |