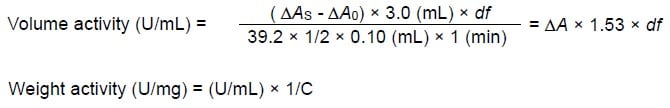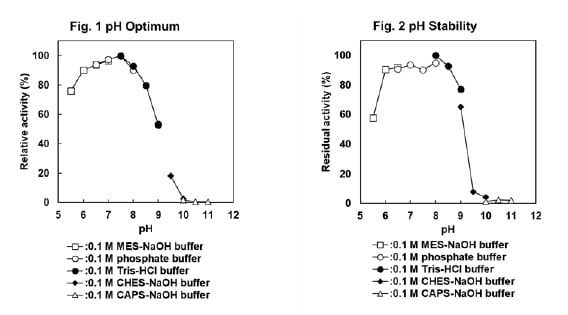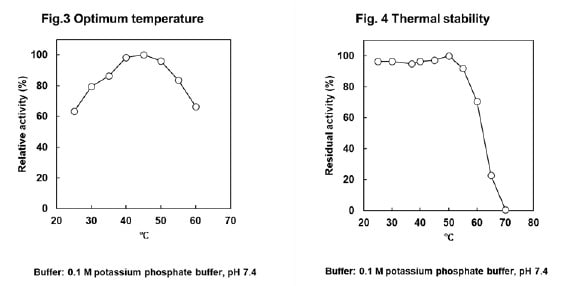
CD : 61227
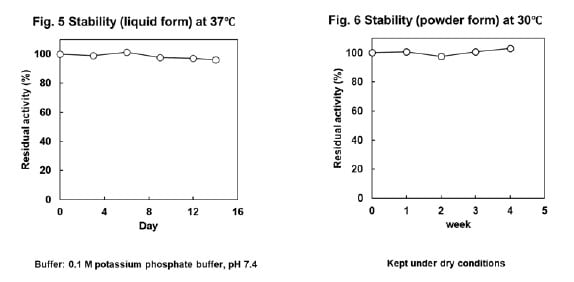
GLOD-E is a FAD-dependent glutamate oxidase has high specificity for glutamate. It is produced using genetic recombination technology, so it is an enzyme with stable quality. Since this enzyme is still under development, please contact us for details.
| Origin | Streptomyces sp. |
|---|---|
| Systematic name | L-glutamate:oxygen oxidoreductase (deaminating) |
| EC Number | 1.4.3.11 |
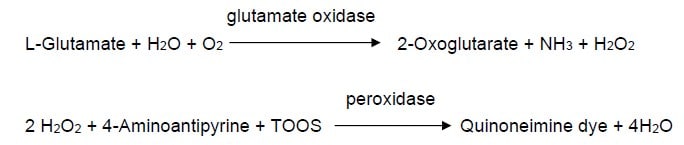
| Reaction formula | L-glutamate + O2 + H2O →→→ 2-oxoglutarate + NH3 + H2O2 |