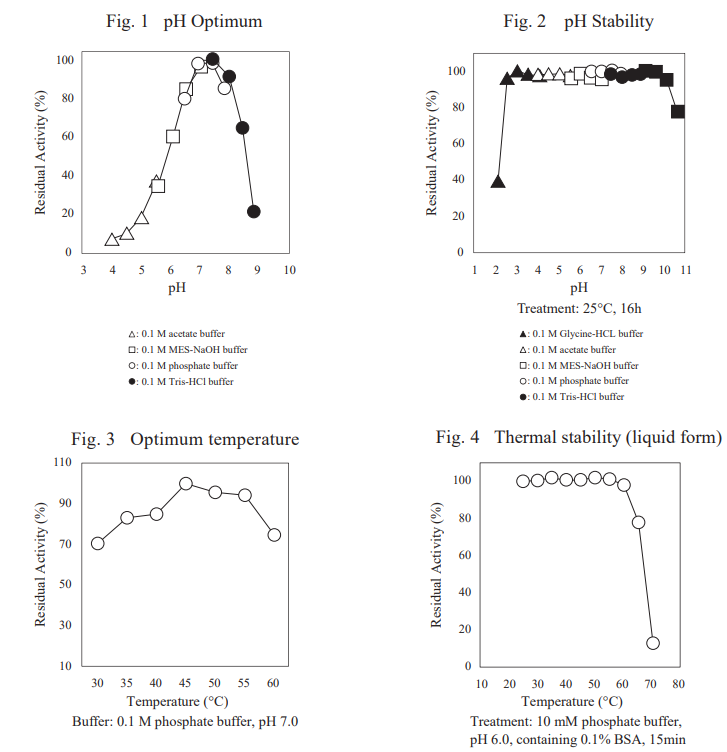
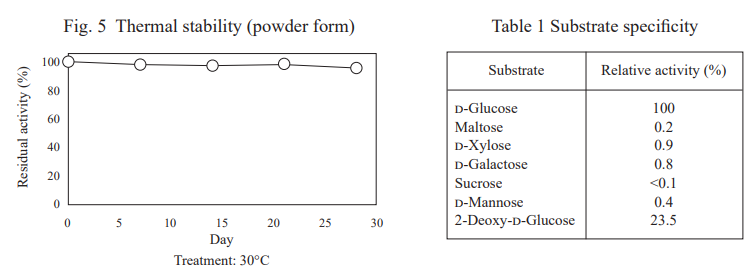
FADGDH-AD is an FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase with low reactivity toward maltose and xylose. It is one of the most stable glucose dehydrogenases for blood glucose measurement and is suitable for continuous glucose monitoring sensor.
| 由来 | recombinant Aspergillus sojae |
|---|---|
| 系统名称 | D-Glucose : acceptor 1-oxidoreductase |
| EC编号 | 1.1.5.9 |
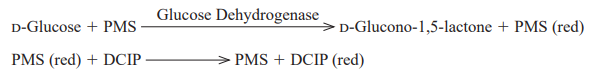
| 反应式 | D-Glucose + acceptor →→→ D-Glucono-1,5-lactone + reduced acceptor |