The enzyme is useful for the determination of creatinine in clinical analysis.
| 由来 | recombinant E. coli |
|---|---|
| 系统名称 | Creatinine amidohydrolase |
| EC编号 | 3.5.2.10 |
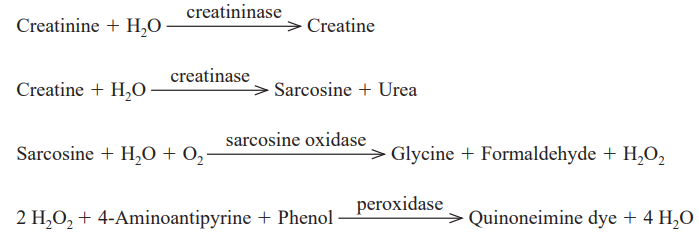
| 反应式 | Creatinine H2O Creatine |

The enzyme is useful for the determination of creatinine in clinical analysis.
| 由来 | recombinant E. coli |
|---|---|
| 系统名称 | Creatinine amidohydrolase |
| EC编号 | 3.5.2.10 |
| 反应式 | Creatinine H2O Creatine |
| Appearance | white lyophilizate | |
|---|---|---|
| Activity | 600-750 U/mg | |
| Contaminants | Catalase ≦0.5 U/U % | |
| Stabilizer | sucrose | |
| Storage condition | below -20℃ |
| Molecular weight | ca. 170 kDa (gel filtration) |
|---|---|
| Structure | 6 subunits of 28 kDa (SDS-PAGE) |
| Isoelectric point | 4.8 |
| Michaelis constant | 3.4×10-2M (creatinine) |
| 4.3×10-2M ((creatine) | |
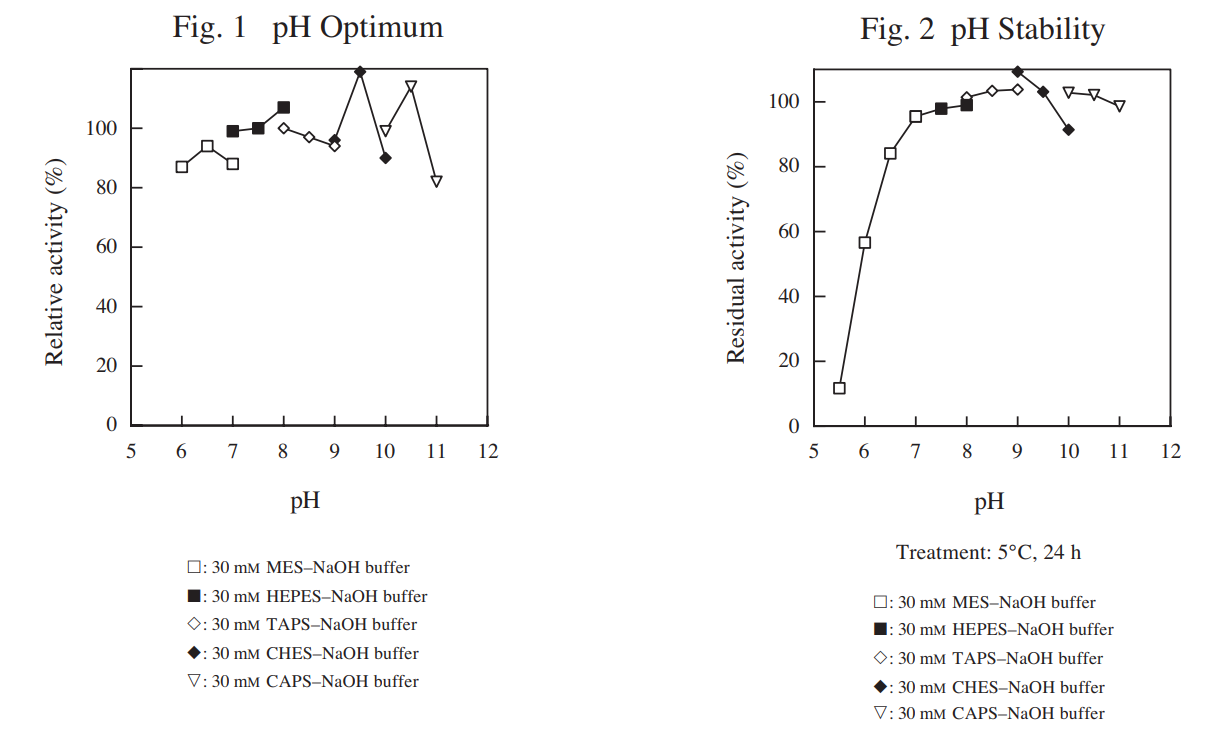
| pH Optimum | 6.5–7.0 (Fig. 1) |
| pH Stability | 7.0–11.0 (Fig. 2) |
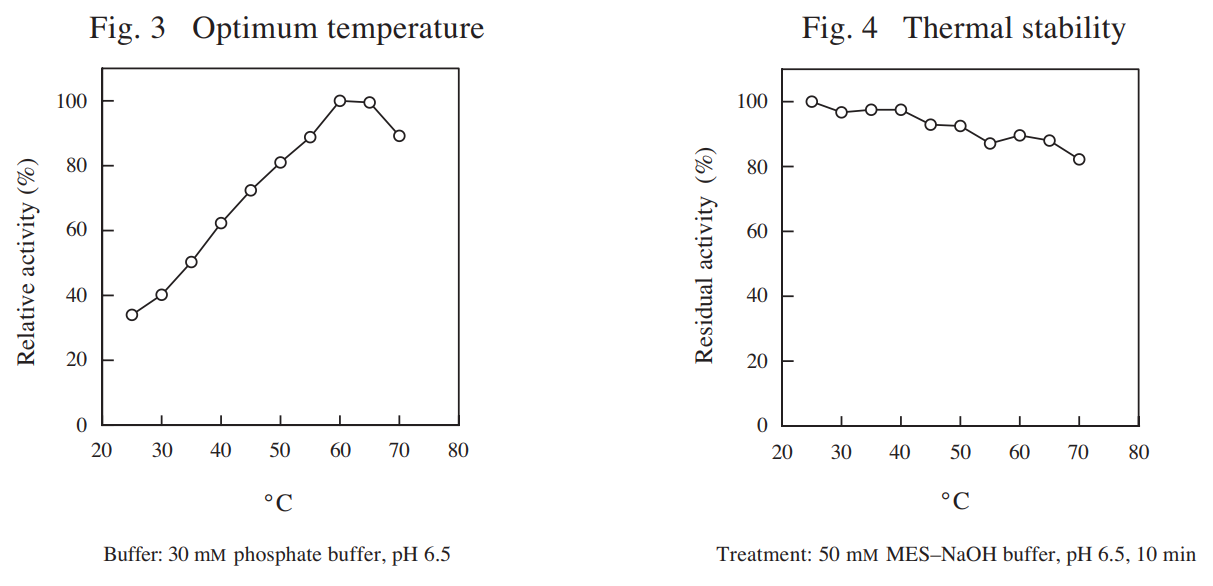
| Optimum temperature | 60–65℃ (Fig. 3) |
| Thermal stability | below 60℃ (Fig. 4) |
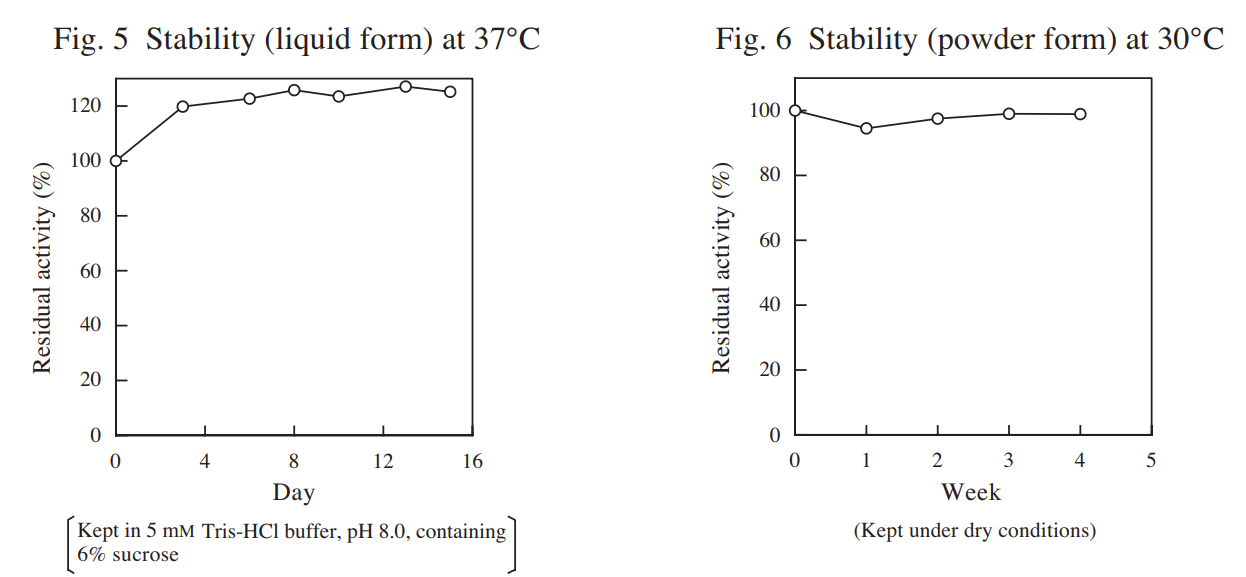
| Stability (liquid form) | stable at 37°C for at least two weeks (Fig. 5) |
| Stability (powder form) | stable at 30°C for at least one month (Fig. 6) |
| Inhibitors | Hg2+ |
| Activators | Mg2+,Mn2+ |
The enzyme is useful for the determination of creatinine and creatine in clinical analysis.
![]()
The appearance of creatine is measured spectrophotometrically at 525 nm.
One unit (U) is defined as the amount of enzyme which produces 1 μmol of creatine per min at 37℃ and pH 6.8 under the conditions described below.
Sample: dissolve the lyophilized enzyme to a volume activity of 2–4 U/ml with ice-cold enzyme dilution buffer (Reagent G) immediately before measurement.
| 0.1 ml | Potassium phosphate buffer | (Reagent A) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.8 ml | Creatinine solution | (Reagent B) |
| 0.1 ml | The terminated solution of step 4 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0.9 ml | Distilled water | |
| 0.5 ml | α-Naphthol solution | (Reagent D) |
| 0.5 ml | Alkaline solution | (Reagent E) |
| 0.5 ml | Diacetyl solution | (Reagent F) |
Activity can be calculated by using the following formula:

Suzuki, M. and Yoshida, M. (1984)
A new enzymatic serum creatinine measurement based on an endogenous creatine-eliminating system
Clinica Chimica Acta, 143, 147–155.